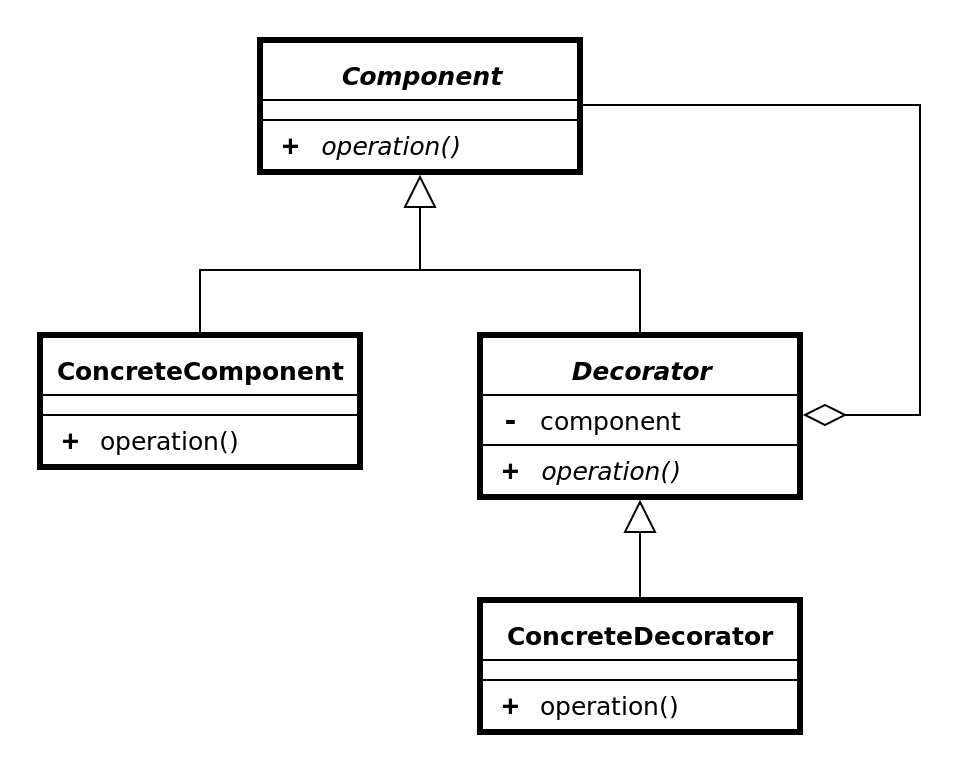
Definition
The Decorator pattern (also known as Wrapper, an alternative naming shared with the Adapter pattern) is a design pattern that allows behavior to be added to an individual object, either statically or dynamically, without affecting the behavior of other objects from the same class. The decorator pattern is often useful for adhering to the Single Responsibility Principle, as it allows functionality to be divided between classes with unique areas of concern.
OCP (Open-Closed Principle)
Software entities (classes, modules, functions, etc.) should be open for extension, but closed for modification. That is, such an entity can allow its behaviour to be extended without modifying its source code.
- Decorator’s super class is Component that is same with the decorated object’s super class.
- Component can be wrapped by multiple decorators.
- Decorator has same super class with Component. So it can has Decorator as a Component.
- Decorator can add new behavior to Component, and it also can execute additional task.
- At runtime, Decorator can be applied at any time when it needs.
Cons
- A lot of ConcreteDecorator classes.
- Initializing object will be complex. Because sometimes it needs to be wrapped by lots of decorators.
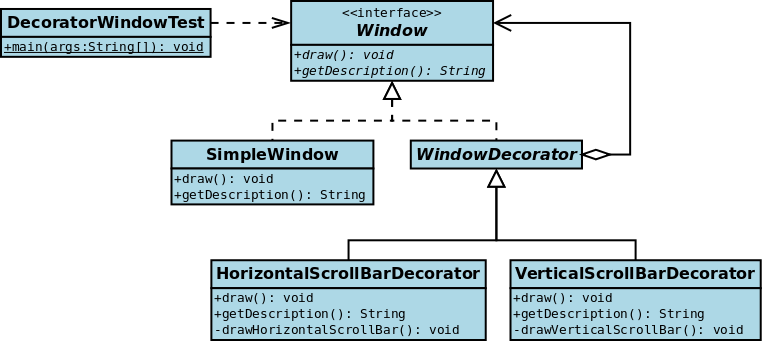
Example
Java I/O is one of the most famous example in Decorator pattern.
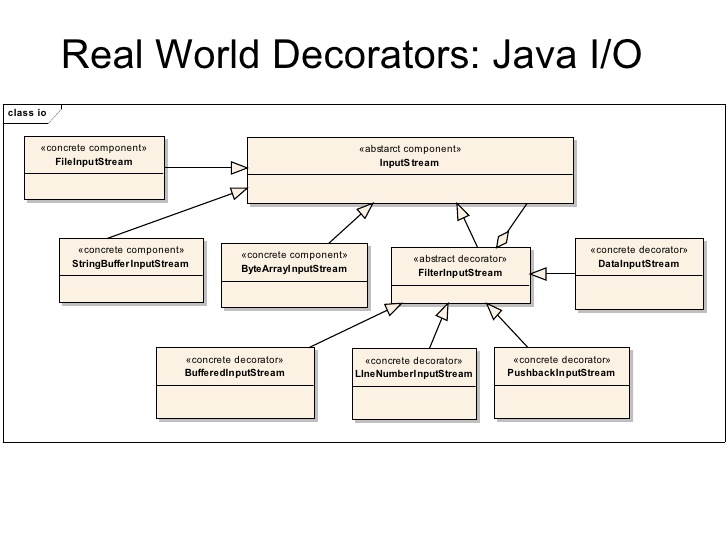
InputStream class is Component.
public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable {
private static final int MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 2048;
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int c = read();
if (c == -1) {
return -1;
}
b[off] = (byte)c;
int i = 1;
try {
for (; i < len ; i++) {
c = read();
if (c == -1) {
break;
}
b[off + i] = (byte)c;
}
} catch (IOException ee) {
}
return i;
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
long remaining = n;
int nr;
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int size = (int)Math.min(MAX_SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE, remaining);
byte[] skipBuffer = new byte[size];
while (remaining > 0) {
nr = read(skipBuffer, 0, (int)Math.min(size, remaining));
if (nr < 0) {
break;
}
remaining -= nr;
}
return n - remaining;
}
public int available() throws IOException {
return 0;
}
public void close() throws IOException {}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
throw new IOException("mark/reset not supported");
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return false;
}
}
FileInputStream is Concrete Component Class
public class FileInputStream extends java.io.InputStream {
private final FileDescriptor fd;
private final String path;
private FileChannel channel = null;
private final Object closeLock = new Object();
private volatile boolean closed = false;
public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null);
}
public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {
String name = (file != null ? file.getPath() : null);
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(name);
}
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (file.isInvalid()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Invalid file path");
}
fd = new FileDescriptor();
fd.attach(this);
path = name;
open(name);
}
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (fdObj == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(fdObj);
}
fd = fdObj;
path = null;
/*
* FileDescriptor is being shared by streams.
* Register this stream with FileDescriptor tracker.
*/
fd.attach(this);
}
private native void open0(String name) throws FileNotFoundException;
private void open(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
open0(name);
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return read0();
}
private native int read0() throws IOException;
private native int readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, off, len);
}
public native long skip(long n) throws IOException;
public native int available() throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (closeLock) {
if (closed) {
return;
}
closed = true;
}
if (channel != null) {
channel.close();
}
fd.closeAll(new Closeable() {
public void close() throws IOException {
close0();
}
});
}
public final FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException {
if (fd != null) {
return fd;
}
throw new IOException();
}
public FileChannel getChannel() {
synchronized (this) {
if (channel == null) {
channel = FileChannelImpl.open(fd, path, true, false, this);
}
return channel;
}
}
private static native void initIDs();
private native void close0() throws IOException;
static {
initIDs();
}
protected void finalize() throws IOException {
if ((fd != null) && (fd != FileDescriptor.in)) {
/* if fd is shared, the references in FileDescriptor
* will ensure that finalizer is only called when
* safe to do so. All references using the fd have
* become unreachable. We can call close()
*/
close();
}
}
}
FilterInputStream is decorator class.
public class FilterInputStream extends java.io.InputStream {
protected volatile java.io.InputStream in;
protected FilterInputStream(java.io.InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return in.read(b, off, len);
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
return in.skip(n);
}
public int available() throws IOException {
return in.available();
}
public void close() throws IOException {
in.close();
}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
in.mark(readlimit);
}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
in.reset();
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return in.markSupported();
}
}
BufferedInputStream is Concrete Decorator class.
public class BufferedInputStream extends java.io.FilterInputStream {
private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;
private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
protected volatile byte buf[];
private static final
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<BufferedInputStream, byte[]> bufUpdater =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater
(BufferedInputStream.class, byte[].class, "buf");
protected int count;
protected int pos;
protected int markpos = -1;
protected int marklimit;
private java.io.InputStream getInIfOpen() throws IOException {
java.io.InputStream input = in;
if (input == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return input;
}
private byte[] getBufIfOpen() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = buf;
if (buffer == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return buffer;
}
public BufferedInputStream(java.io.InputStream in) {
this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
public BufferedInputStream(java.io.InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
pos = 0; /* no mark: throw away the buffer */
else if (pos >= buffer.length) /* no room left in buffer */
if (markpos > 0) { /* can throw away early part of the buffer */
int sz = pos - markpos;
System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz);
pos = sz;
markpos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */
pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */
} else if (buffer.length >= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE) {
throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");
} else { /* grow buffer */
int nsz = (pos <= MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - pos) ?
pos * 2 : MAX_BUFFER_SIZE;
if (nsz > marklimit)
nsz = marklimit;
byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz];
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos);
if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) {
// Can't replace buf if there was an async close.
// Note: This would need to be changed if fill()
// is ever made accessible to multiple threads.
// But for now, the only way CAS can fail is via close.
// assert buf == null;
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
buffer = nbuf;
}
count = pos;
int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);
if (n > 0)
count = n + pos;
}
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
int avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0) {
/* If the requested length is at least as large as the buffer, and
if there is no mark/reset activity, do not bother to copy the
bytes into the local buffer. In this way buffered streams will
cascade harmlessly. */
if (len >= getBufIfOpen().length && markpos < 0) {
return getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len);
}
fill();
avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0) return -1;
}
int cnt = (avail < len) ? avail : len;
System.arraycopy(getBufIfOpen(), pos, b, off, cnt);
pos += cnt;
return cnt;
}
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len)
throws IOException
{
getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream
if ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = 0;
for (;;) {
int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);
if (nread <= 0)
return (n == 0) ? nread : n;
n += nread;
if (n >= len)
return n;
// if not closed but no bytes available, return
java.io.InputStream input = in;
if (input != null && input.available() <= 0)
return n;
}
}
public synchronized long skip(long n) throws IOException {
getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
long avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0) {
// If no mark position set then don't keep in buffer
if (markpos <0)
return getInIfOpen().skip(n);
// Fill in buffer to save bytes for reset
fill();
avail = count - pos;
if (avail <= 0)
return 0;
}
long skipped = (avail < n) ? avail : n;
pos += skipped;
return skipped;
}
public synchronized int available() throws IOException {
int n = count - pos;
int avail = getInIfOpen().available();
return n > (Integer.MAX_VALUE - avail)
? Integer.MAX_VALUE
: n + avail;
}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
marklimit = readlimit;
markpos = pos;
}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
getBufIfOpen(); // Cause exception if closed
if (markpos < 0)
throw new IOException("Resetting to invalid mark");
pos = markpos;
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
public void close() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer;
while ( (buffer = buf) != null) {
if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, null)) {
InputStream input = in;
in = null;
if (input != null)
input.close();
return;
}
// Else retry in case a new buf was CASed in fill()
}
}
}
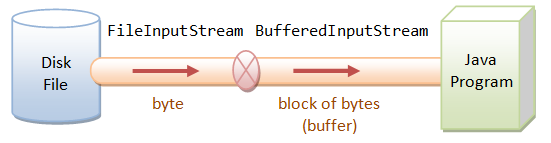
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("path");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bis.read()
FileInputStream is InputStream that can read data from file. And BufferedInputStream is a decorator of InputStream that has a buffer to optimize performance. It reads many bytes at a time from the stream to buffer. When you execute above code, then file will be read through the buffer like below.
functional style
If the Component has single abstract method, then we can easily implements decorator pattern with chaining of lambda expressions. Below example is closer to Builder pattern that is usually used with Decorator pattern.
Component
public interface Beverage {
public abstract String getDescription();
public abstract double cost();
}
Concrete Component
public class Espresso implements Beverage {
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "espresso";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return 1.99;
}
}
Decorator
public abstract class CondimentDecorator implements Beverage {
Beverage beverage;
protected CondimentDecorator(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
}
Concrete Decorator
public class Mocha extends CondimentDecorator {
protected Mocha(Beverage beverage) {
super(beverage);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", mocha";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return 0.2 + beverage.cost();
}
}
public class Whip extends CondimentDecorator {
protected Whip(Beverage beverage) {
super(beverage);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", whip";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return 0.3 + beverage.cost();
}
}
functional style helper
public interface DecoratingBeverage extends Beverage {
static DecoratingBeverage from(Beverage beverage) {
return new DecoratingBeverage() {
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription();
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return beverage.cost();
}
};
}
default DecoratingBeverage decorate(Function<? super DecoratingBeverage, ? extends Beverage> decorator) {
Beverage beverage = decorator.apply(this);
return from(beverage);
}
}
use case
public class Order {
static void print(Beverage beverage) {
System.out.println(beverage.getDescription() + " $" + beverage.cost());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Beverage newOrderedBeverage = DecoratingBeverage.from(new Espresso())
.decorate(beverage -> new Mocha(beverage))
.decorate(beverage -> new Whip(beverage));
print(newOrderedBeverage);
}
}