Adapter Pattern
Definition
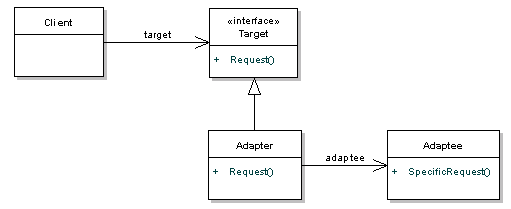
The adapter pattern is a software design pattern (also known as Wrapper, an alternative naming shared with the Decorator pattern) that allows the interface of an existing class to be used as another interface. It is often used to make existing classes work with others without modifying their source code.
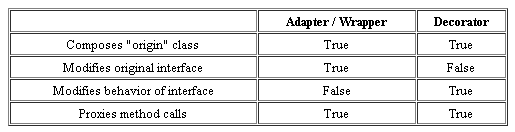
Both Adapter pattern and Decorator pattern is usually called as Wrapper. But the purpose is basically different. At decorator pattern, we usually add additional function to original interface. At Adapter pattern, It is convert the interface to existing one.
Implementation
Duck
public interface Duck {
public void quack();
public void fly();
}
Turkey
public interface Turkey {
public void gobble();
public void fly();
}
Wild Turkey
public class WildTurkey implements Turkey {
@Override
public void gobble() {
System.out.println("Gobble gobble");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("I'm flying a short distance");
}
}
TurkeyAdapter
public class TurkeyAdapter implements Duck {
Turkey turkey;
public TurkeyAdapter(Turkey turkey) {
this.turkey = turkey;
}
@Override
public void quack() {
turkey.gobble();
}
@Override
public void fly() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
turkey.fly();
}
}
}
Demo
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WildTurkey wildTurkey = new WildTurkey();
Duck tuckeyAdapter = new TurkeyAdapter(wildTurkey);
tuckeyAdapter.quack();
tuckeyAdapter.fly();
}
}
Facade Pattern
Definition
The Facade design pattern is often used when a system is very complex or difficult to understand because the system has a large number of interdependent classes or its source code is unavailable. This pattern hides the complexities of the larger system and provides a simpler interface to the client. It typically involves a single wrapper class which contains a set of members required by client. These members access the system on behalf of the facade client and hide the implementation details
A Facade can
- make a software library easier to use, understand and test, since the facade has convenient methods for common tasks
- make the library more readable, for the same reason
- reduce dependencies of outside code on the inner workings of a library, since most code uses the facade, thus allowing more flexibility in developing the system
- wrap a poorly designed collection of APIs with a single well-designed API
Implementation
public class EncodingOptionParser {
public EncodingOption parse(String option) {
System.out.println("parse option.. " + option);
return new EncodingOption();
}
}
public class TranscodeEngineConnector {
public class Engine {
// this is sample
}
Engine engine;
public TranscodeEngineConnector() {
this.engine = new Engine();
}
public void connect() {
System.out.println("Connect to Transcoder Engine..");
}
public void validate(String path) {
System.out.println("Validating Source " + path + " ..");
}
public void optimizeOption(EncodingOption encodingOption) {
System.out.println("Optimizing Option..");
}
public String encode() {
System.out.println("Encoding..");
return "localOutputPath";
}
}
public class FileTransfer {
public void copy(String source, String dest) {
System.out.println("copying result..");
}
}
public class EncodeTask {
private String id;
private String sourcePath;
private String destPath;
private String option;
...
}
public class TranscodeFacade {
EncodingOptionParser encodingOptionParser;
TranscodeEngineConnector transcodeEngineConnector;
FileTransfer fileTransfer;
public TranscodeFacade(EncodingOptionParser encodingOptionParser, TranscodeEngineConnector transcodeEngineConnector, FileTransfer fileTransfer) {
this.encodingOptionParser = encodingOptionParser;
this.transcodeEngineConnector = transcodeEngineConnector;
this.fileTransfer = fileTransfer;
}
public void encode(EncodeTask task) {
EncodingOption encodingOption = encodingOptionParser.parse(task.getOption());
transcodeEngineConnector.connect();
transcodeEngineConnector.validate(task.getSourcePath());
transcodeEngineConnector.optimizeOption(encodingOption);
String outputPath = transcodeEngineConnector.encode();
fileTransfer.copy(outputPath, task.getDestPath());
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EncodeTask encodeTask = new EncodeTask();
encodeTask.setId("id1");
encodeTask.setSourcePath("source");
encodeTask.setDestPath("dest");
encodeTask.setOption("option json string");
TranscodeEngineConnector transcodeEngineConnector = new TranscodeEngineConnector();
EncodingOptionParser encodingOptionParser = new EncodingOptionParser();
FileTransfer fileTransfer = new FileTransfer();
TranscodeFacade transcodeFacade = new TranscodeFacade(encodingOptionParser, transcodeEngineConnector, fileTransfer);
transcodeFacade.encode(encodeTask);
}
}