State Pattern
Definition
The compound pattern is that combines at least two patterns into a solution that solves a recurring or general problem. For example, Model–view–controller (MVC) pattern for implementing user interfaces on computers. It divides a given software application into three interconnected parts, so as to separate internal representations of information from the ways that information is presented to or accepted from the user.
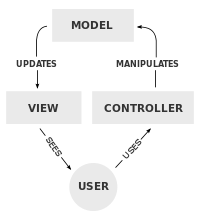
Components
A typical collaboration of the MVC components.
- The model is the central component of the pattern. It expresses the application’s behavior in terms of the problem domain, independent of the user interface. It directly manages the data, logic and rules of the application.
- A view can be any output representation of information, such as a chart or a diagram. Multiple views of the same information are possible, such as a bar chart for management and a tabular view for accountants.
- The controller, accepts input and converts it to commands for the model or view.
Interactions
- A model stores data that is retrieved according to commands from the controller and displayed in the view.
- A view generates new output to the user based on changes in the model.
- A controller can send commands to the model to update the model’s state. It can also send commands to its associated view to change the view’s presentation of the model.