Overview
- Actually, i attended hadoop summit 2016 - tokyo at last month. So i am going to review some of the talks that i heard. Also you can download slides and watch the videos from youtube.
- slides
- youtube
- Unfortunately, just keynote videos were uploaded now. But i think each session’s video will be uploaded soon.
- This article is about opening keynote at 2nd day.
10 Years of Apache Hadoop and Beyond
You can watch the video at youtube. The speaker of this talk is Sanjay Radia (Chief Architect, Co-Founder at Hortonworks).
Hadoop journey
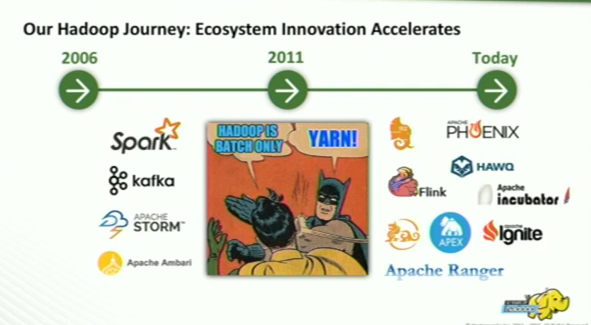
- 2006 : HDFS, MapReduce
- parallel computing
- tera-bytes scale of data
- 2011 : Yarn
- Hadoop was for batch only, MapReduce paradigm
- become to true data platform that is interactive, realtime application
- Today
Hive (SQL & Hadoop)
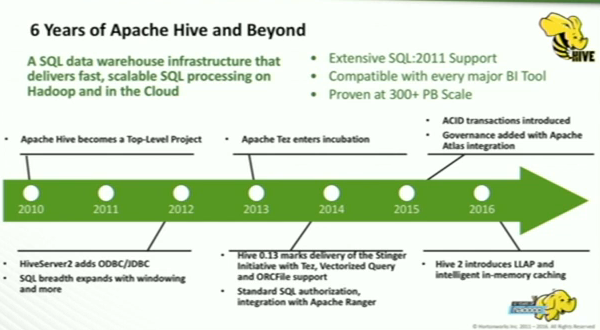
- 2010 : Apache Hive becomes a Top-Level Project
- 2012 : ODBC, JDBC, batch to interactive
- 2013 : TEZ, performance, MapReduce implementation to native
- 2014 : Apache Ranger
- 2015 : ACID, continuous ingestion, Apache Atlas
- 2016 : LLAP, in-memory caching
Hive 2 With LLAP
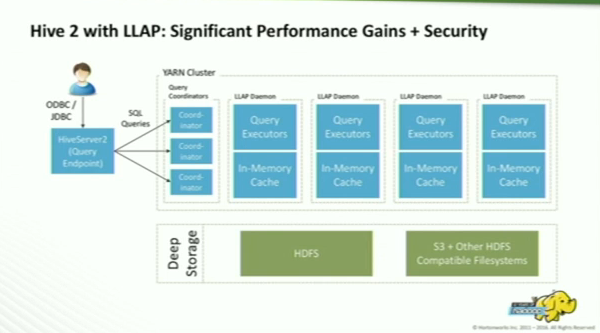
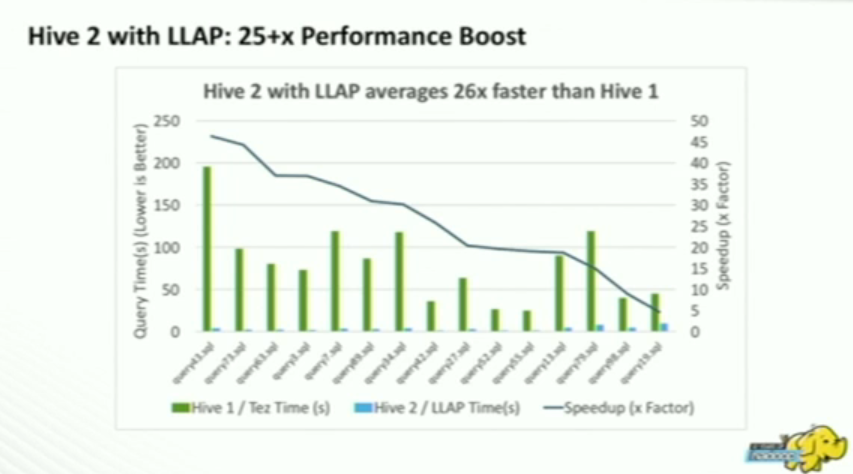
- Performance improvement
- daemon for executing threads
- process creation to thread creation
- instruction cache
- caches only data in use, and it can cache from anywhere
- Security
- fine grained access control
Hadoop Eco Systems to the Cloud!
Why Hadoop in the Cloud?
Cloud can saves your money and time. You only pay for what you use. And Cloud is flexible to use. If you want to do a short task, then you can choose ephemeral clusters and do the task, then shut it down to stop the meter. Also if offers a lot of elasticity, which means you can scale up and down on demand all computes node. And storage is also scalable.
Key Architectural Considerations for Hadoop in the Cloud
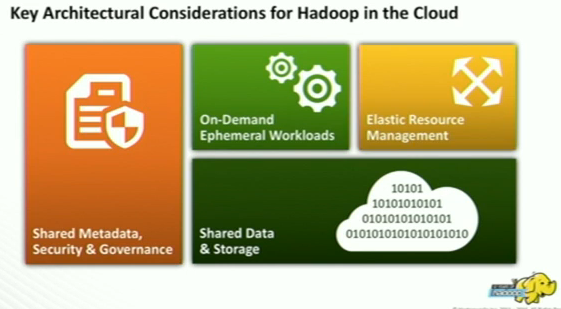
Shared Data & Storage
- Shared data lake is the cloud storage not HDFS, of specfic hadoop cluster.
- Each cluster has its own data lake, and data lake is cloud storage.
- Data lake is available not just to hadoop apps, it also available to cloud native apps.
- Cloud storage has two key limitations.
- It offers eventual consistency.
- API is not what most traditional applications expect.
- Cloud storage was designed for two things. Low-cost and Scale. Performance is not strong point. It segregated from compute, therefore you gonna get slower performance. And therefore memory and local storage has different roles, that of caching. It enhance the performance.
Enhance Performance via Caching
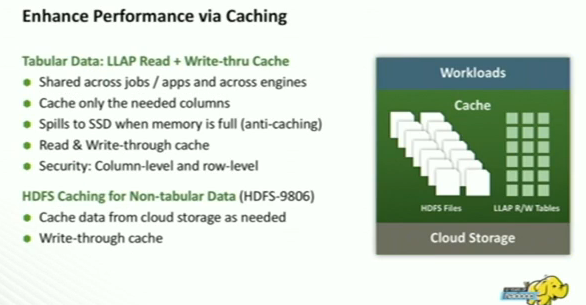
- For tabular data, LLAP
- For non-tabular data, HDFS can be used
Prescriptive On-Demand Ephemeral Workloads
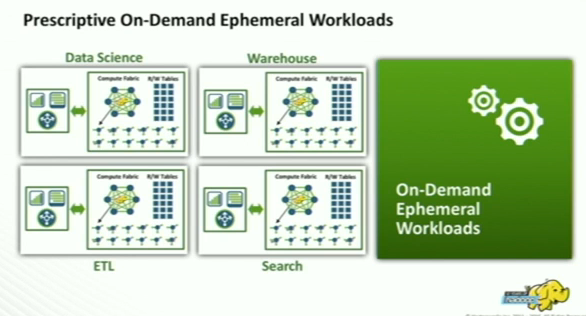
Shared Data requires Shared Metadata, Security and Governance
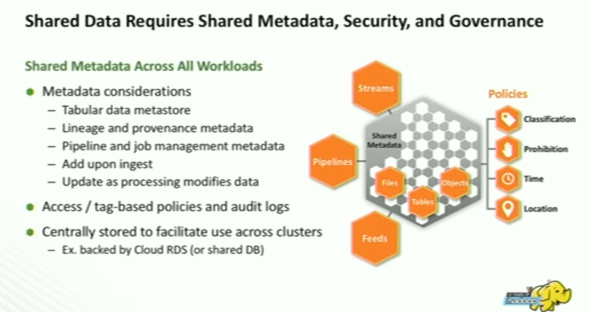
- In the Cloud world, each ephemeral cluster cannot have its own copy of prior metadata.
- It need to be stored centrally on the cloud database, and it need to be accessible to all the clusters.
- Security and Governance metadata also need to be centrally stored and access. Therefore Apache Ranger & Atlas is proposed for that functionality.
Elastic Resource Management in Context of Workloads

- Resource is elastic!
- Previously yarn focus on cluster management.
- Yarn scheduler needs to manage resources in the context of workloads, and meeting the SLAs.
- Pricing-aware is new dimension.