State Pattern
Definition
The state pattern is a behavioral software design pattern that implements a state machine in an object-oriented way. With the state pattern, a state machine is implemented by implementing each individual state as a derived class of the state pattern interface, and implementing state transitions by invoking methods defined by the pattern’s superclass.
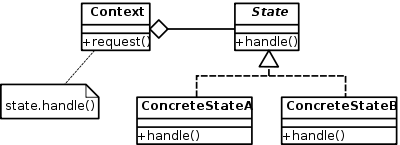
Implementation
State Interface & Concrete class
public interface State {
void insertQuarter();
void ejectQuarter();
void turnCrank();
void dispense();
}
public class HasQuarterState implements State {
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
@Override
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("cannot insert");
}
@Override
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("quarter is ejected");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
}
@Override
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("turned crank");
int winner = random.nextInt(10);
if ((winner == 0) && (gumballMachine.getCount() > 1)) {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getWinnerState());
} else {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldState());
}
}
@Override
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("cannot dispense");
}
}
public class NoQuarterState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
@Override
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("quarter is inserted");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getHasQuarterState());
}
@Override
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("insert qaurter");
}
@Override
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("insert qaurter");
}
@Override
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("insert qaurter");
}
}
public class SoldOutState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public SoldOutState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
@Override
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("cannot insert");
}
@Override
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("cannot eject");
}
@Override
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("cannot turn crank");
}
@Override
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("cannot dispense");
}
}
public class SoldState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public SoldState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
@Override
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("cannot insert");
}
@Override
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("cannot eject");
}
@Override
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("cannot turn");
}
@Override
public void dispense() {
gumballMachine.releaseBall();
if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
} else {
System.out.println("out of gumballs");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
}
}
}
public class WinnerState implements State {
GumballMachine gumballMachine;
public WinnerState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {
this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;
}
@Override
public void insertQuarter() {
System.out.println("cannot insert");
}
@Override
public void ejectQuarter() {
System.out.println("cannot eject");
}
@Override
public void turnCrank() {
System.out.println("cannot turn crank");
}
@Override
public void dispense() {
System.out.println("Congratulations, you can get one more gumball");
gumballMachine.releaseBall();
if (gumballMachine.getCount() == 0) {
System.out.println("out of gumballs");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
} else {
gumballMachine.releaseBall();
if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());
} else {
System.out.println("out of gumballs");
gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());
}
}
}
}
Context
public class GumballMachine {
State soldOutState;
State noQuarterState;
State hasQuarterState;
State soldState;
State winnerState;
State state = soldOutState;
int count = 0;
public GumballMachine(int numberGumballs) {
soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);
noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);
hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);
soldState = new SoldState(this);
winnerState = new WinnerState(this);
this.count = numberGumballs;
if (numberGumballs > 0) {
state = noQuarterState;
}
}
public void insertQuarter() {
state.insertQuarter();
}
public void ejectQuarter() {
state.ejectQuarter();
}
public void turnCrank() {
state.turnCrank();
state.dispense();
}
void setState(State state) {
this.state = state;
}
void releaseBall() {
System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot..");
if (count != 0) {
count = count -1;
}
}
public State getWinnerState() {
return winnerState;
}
public void setWinnerState(State winnerState) {
this.winnerState = winnerState;
}
public State getSoldOutState() {
return soldOutState;
}
public State getNoQuarterState() {
return noQuarterState;
}
public State getHasQuarterState() {
return hasQuarterState;
}
public State getSoldState() {
return soldState;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Gumball Machine!! Current Gumball : " + count;
}
}
Demo
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GumballMachine gumballMachine = new GumballMachine(5);
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
gumballMachine.insertQuarter();
gumballMachine.turnCrank();
System.out.println(gumballMachine);
}
}
Proxy Pattern
Definition
A proxy, in its most general form, is a class functioning as an interface to something else. The proxy could interface to anything: a network connection, a large object in memory, a file, or some other resource that is expensive or impossible to duplicate. In short, a proxy is a wrapper or agent object that is being called by the client to access the real serving object behind the scenes. Use of the proxy can simply be forwarding to the real object, or can provide additional logic. In the proxy extra functionality can be provided, for example caching when operations on the real object are resource intensive, or checking preconditions before operations on the real object are invoked. For the client, usage of a proxy object is similar to using the real object, because both implement the same interface.
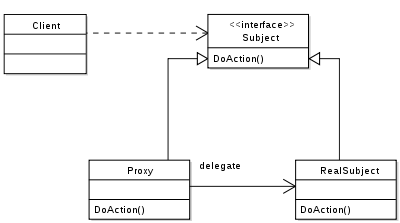
Remote Proxy
In distributed object communication, a local object represents a remote object (one that belongs to a different address space). The local object is a proxy for the remote object, and method invocation on the local object results in remote method invocation on the remote object. An example would be an ATM implementation, where the ATM might hold proxy objects for bank information that exists in the remote server.
Virtual Proxy
In place of a complex or heavy object, a skeleton representation may be advantageous in some cases. When an underlying image is huge in size, it may be represented using a virtual proxy object, loading the real object on demand.
Protection Proxy
A protection proxy might be used to control access to a resource based on access rights.
Implementation
This is protection proxy example that controls access to a resource
Proxy Target
public interface PersonBean {
String getName();
String getGender();
String getInterests();
int getHotOrNotRating();
void setName(String name);
void setGender(String gender);
void setInterests(String interests);
void setHotOrNotRating(int rating);
}
public class PersonBeanImpl implements PersonBean {
String name;
String gender;
String interests;
int rating;
int ratingCount = 0;
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
@Override
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String getInterests() {
return interests;
}
@Override
public void setInterests(String interests) {
this.interests = interests;
}
@Override
public int getHotOrNotRating() {
return (ratingCount == 0) ? 0 : rating / ratingCount;
}
@Override
public void setHotOrNotRating(int rating) {
this.rating += rating;
ratingCount++;
}
}
Invocation Handler
public class OwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
PersonBean personBean;
public OwnerInvocationHandler(PersonBean personBean) {
this.personBean = personBean;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) {
return method.invoke(personBean, args);
} else if (method.getName().equals("setHotOrNotRating")) {
throw new IllegalAccessException();
} else if (method.getName().startsWith("set")) {
return method.invoke(personBean, args);
}
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
public class NonOwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
PersonBean personBean;
public NonOwnerInvocationHandler(PersonBean personBean) {
this.personBean = personBean;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) {
return method.invoke(personBean, args);
} else if (method.getName().equals("setHotOrNotRating")) {
return method.invoke(personBean, args);
} else if (method.getName().startsWith("set")) {
throw new IllegalAccessException();
}
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
Demo
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PersonBean joe = search("joe");
PersonBean ownerProxy = getOwnerProxy(joe);
System.out.println("Name is " + ownerProxy.getName());
ownerProxy.setInterests("skiing");
System.out.println("Interest set from owner proxy");
try {
ownerProxy.setHotOrNotRating(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Cannot set rating from owner proxy");
}
System.out.println("Rating is " + ownerProxy.getHotOrNotRating());
PersonBean nonOwnerProxy = getNonOwnerProxy(joe);
System.out.println("Name is " + nonOwnerProxy.getName());
try {
nonOwnerProxy.setInterests("skiing");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Cannot set interests from non owner proxy");
}
nonOwnerProxy.setHotOrNotRating(3);
System.out.println("Rating set from non owner proxy");
System.out.println("Rating is " + nonOwnerProxy.getHotOrNotRating());
}
private static PersonBean getOwnerProxy(PersonBean personBean) {
return (PersonBean) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
personBean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
personBean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new OwnerInvocationHandler(personBean)
);
}
private static PersonBean getNonOwnerProxy(PersonBean personBean) {
return (PersonBean) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
personBean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
personBean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new NonOwnerInvocationHandler(personBean)
);
}
private static PersonBean search(String name) {
PersonBeanImpl personBean = new PersonBeanImpl();
personBean.setName(name);
personBean.setGender("male");
personBean.setInterests("programming");
personBean.setHotOrNotRating(10);
return personBean;
}
}